wiiw Forecast Reports
CESEE overview: Robust growth in the face of increased negative risks
publication_icon
in: Strong Growth Amid Increased Negative Risks
wiiw Forecast Report No. Autumn 2018, November 2018 , pp. 14-27
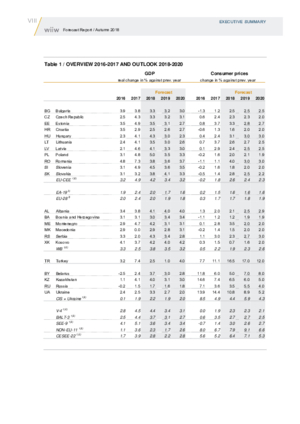
- Across most of the region, growth will still be quite strong by post-crisis standards during the forecast period. Private consumption will remain the key growth driver as tight labour markets will further push up wages. High levels of capacity utilisation will spur increases in investment.
- However, 2018 has brought a slowdown in the GDP dynamics of most of the countries, with Turkey standing out as the worst-performing country. All the EU-CEE economies, apart from Hungary, Poland and Slovakia, started on the path of deceleration, with the biggest adjustment in the growth rate – 3 percentage points – taking place in Romania.
- A loss of momentum in the eurozone and other advanced economies presents a challenge to growth in CESEE– especially in those that are strongly integrated into the regional production chains and rely on exports in their growth models. This will become particularly apparent by the end of our forecast period: we have revised down our forecasts for 2020 for many countries, in particular for the EU-CEE sub-region.
- Domestic factors will also contribute to lower growth rates in the CESEE region, as the currently strong (for most) cyclical upswing fades. Only a few Western Balkan economies will keep up their current pace of growth, though that will remain rather moderate and not enough for significant convergence with wealthier parts of EU-CEE or Western Europe. Turkey will also bounce back from its current difficulties by 2020.
- Russia will remain the economy facing the biggest challenges, and will continue to post very disappointing growth rates during the forecast period. In part, this will reflect the impact of international sanctions, although the main reasons for Russia’s weak growth performance are domestic and structural in nature. Its problems will have negative spill-over effects for the rest of the CIS region as well.
Reference to wiiw databases: wiiw Annual Database, wiiw Monthly Database